Use of monoclonal antibodies has expanded into the field of asthma with an FDA approved drug Benralizumab, a somewhat add-on asthma treatment for those who suffer specifically from eosinophilic asthma. The severity of this particular form of asthma is traced to an excess of white blood cells in an individual that increases inflammatory responses in the body, in this case the chronic inflammation is seen in the lungs and the tissue of that individual’s respiratory system. After offering a brief introduction into the world of monoclonal antibodies, it will become clear how perfect Benralizumab is for the job of fighting the overactive immune response. After all, it’s what they were made for.
I’m not even an artist, but I think understanding monoclonal antibodies is somewhat like understanding someone mixing paints colors to make the perfect picture. Say you want a beautiful pink color to paint a pig, the focal point of your drawing, but you only have red and white on your palette. Although without the added pressure of one’s life depending on it, this scenario is at its core similar to when the human body needs a certain antibody to fight off an antigen, and is looking at its palette containing B cells and Myeloma cells. Just as the red brings the dark heart of the color, B cells offer the capacity to make antibodies. Just as the white color brings the lightness to the color, myeloma cells bring plasma cells with the capacity to grow indefinitely, and are specifically susceptible to a drug known as aminopterin. Just like mixing paints, the making of monoclonal antibodies involves mixing together these qualities of B cells and myeloma cells to make a new cell with its own unique capacities. This “pink” is a hybridoma cell.

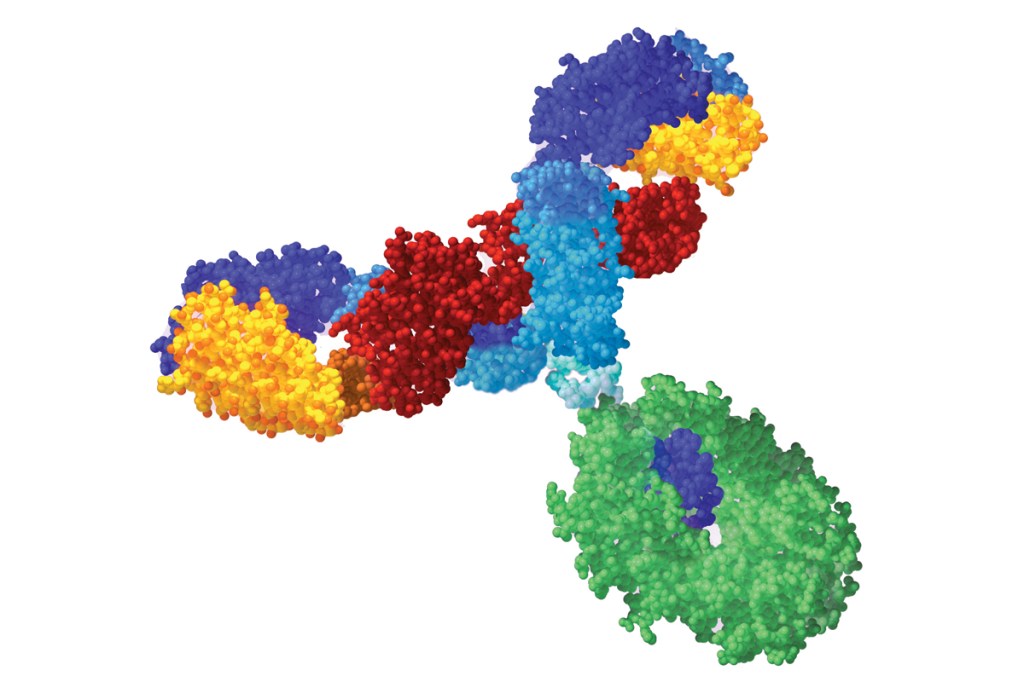
As no color mix is perfect, there’s usually a part of the paint mix that’s a little lighter or darker than another part, one of these fitting perfectly for your painting vision of the pig you set out to craft. This is similar to the production of hybridoma cells. As these fusion cells are made, there is one that fits perfectly with the antigen being targeted. It’s this hybridoma cell that will replicate and produce antibodies, just as it is that specific shade of pink you will select with your brush and spread on your canvas. The antibodies, being identical to one another, are able to fight off the particular antigen with maximum efficiency.
In the case of Benralizumab, the monoclonal antibody used for fighting eosinophilic asthma, specifically fights the excess production of eosinophil cells in the body that happen in response to an asthma trigger, causing severe inflammatory response of the airways and respiratory routes, leading to asthma symptoms. When these antibodies bind to the excess eosinophils they then can signal to the body’s immune system that these cells must be removed. The most extreme side effects of this drug are allergic hypersensitivity reactions, even days after an individual is injected with the drug. The most common side effects, however, consist of a sore throat and headache. Pregnancy and parasitic/helminth infections serve as preexisting conditions that increase dangers of using Benralizumab. It is also key to NOT stop taking other asthma medicine.
EXTRA CREDIT
As a history minor, I am passionate about the importance of fully understanding a situation by looking to the past. In other words, placing things in historical context. As the world of science continues to do everything in their power to move us forward, I will take us back about 100 years, to another period in history in which a virus was taking over the normalcy of America. The Polio epidemic, somewhat similar to the COVID-19 presence in America, had a strong center presence in New York. This epidemic took the lives of around 6,000 individuals, paralyzing those it did not kill. Also similar to today’s handling of COVID-19, this summertime epidemic brought a temporary end to things like pool time and gatherings.
Scientists reflect on this outbreak as an example of the importance of vaccination, as this disease went from one of the most feared diseases in the nation to eradicated since 1979. Traveling to other countries, where there is NOT herd immunity, increases the risk of obtaining this disease, as the US vaccination success has prevented the possibility of individuals being hosts of the disease.